THE INFLUENCE OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ON EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE OF MICROFINANCE BANKS
Aim and Objectives of the Study: The main objective of the study is to examine the influence of organizational culture on employee performance of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
Other objectives of the study are:
1) To examine the relationship between Team Work and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
2) To examine the relationship between Team Work and Customers Satisfaction of Micro Finance Banks in Port Harcourt.
3) To examine the relationship between Competitiveness and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
4) To examine the relationship between Competitiveness and Customer Satisfaction of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of the Study
Culture is the arrangement of different attributes that express an organization and differentiate the firm from another one (Forehand and von Gilmer, 1964). According to Hofstede (1980), culture is the collective thinking of minds which creates a difference between the members of one group from another. As per Schein (1990), culture is a set of different values and behaviors that may be considered a guide to success. According to Kotter and Heskett (1992), culture means a fairly established set of beliefs, behaviors, and values of society contain generally. In simple words, we can understand that culture is gained through knowledge, explanations, values, beliefs, communication, and behaviors of a large group of people, at the same time and same place.
Organizational culture is a system of values, traditions, and rules, shared by all of the organization’s members, and every business organization has a particular culture that expresses its personality according to Yassin (2010). Organizational culture plays a primary function in modeling the behavior and performance of the firm through the collective efforts of individual members of the organization. The cultural idea must be learned and shared in the organizations (Titiev, 1959). Pettigrew (1979), argues that the cultures of organizations are based on cognitive systems which help to explain how employees think and make decisions. He also noted the different levels of culture based on the multifaceted set of beliefs, values, and assumptions that determine the ways organizations conduct their business. According to Tichy (1982), organizational culture is known as “normative glue” which means to hold the overall organization together. The concept of organizational culture also makes available a base for determining the differentiation that may survive in-between the organizations that are doing business in the same national culture (Schein, 1990). Some works of literature have commonly identified Clan culture as a type of organizational culture that is based on mentoring, nurturing, and participation and is also referred to as extended family or large family. It is a working environment that is friendly, people have a lot in common. The leaders or executives are seen as mentors or maybe as father figures. It is held together by loyalty and tradition as great participation. Emphasis is on long-term human resources development and bonding colleagues by morale. Success here is defined within the framework of meeting client needs and caring for people. Another is a result-based organization that emphasizes finishing work and getting things done. People are competitive and focused on goals. Leaders are seen as hard drivers, producers, and rivals at the same time, they are tough and have high expectations. The emphasis on winning keeps the organization together. Reputation and success are the most important, market penetration and stocks are the definitions of success, and competitive prices and market leadership are important. The organizational style is based on competition. Adhocracy (creative) is a developmental organizational culture that is based on risk-taking, innovation, and change, Quinn, and Spretzer (1991). It refers to the culture of an organization in entrepreneurial flexible, innovative and creative areas with its external-oriented and dynamic structure. Employees can take the initiative supported with discoveries and freedom so they feel satisfied, happy, and successful in the environment. Organizations whose businesses are basically on the internet with advanced technology are examples of this culture. While Hierarchy culture is a formalized and structured work environment, procedures decide what people do. Leaders are proud of their efficiency-based coordination and organization. Keeping the organization functioning smoothly is most crucial. Formal rules and policies keep the organization together. The long-term goals are stability and results paired with the efficient and smooth execution of tasks. Trustful delivery, smooth planning, and low costs define success. However, for simplicity of this research some organizational culture style that defines teamwork, and competition-based cultures will be considered in detail.
Teamwork is a precise organizational measure that shows many different features in all types of organizations including non – profit (Mulika, 2010). Conti and Kleiner (2003) reported that teams offer greater participation, challenges, and feelings of accomplishment. Some companies have started to apply a team-based strategy in their work performance to maintain the productivity of their workers and to emphasize the importance of working together as one united entity to achieve the objectives and goals of the organization in the best way possible. Team-based strategy means a basic method followed by the members of an organization to work in teams to finish the required tasks. As a result of such strategies applied in workplaces, the managers of such organizations are clarifying the significance of teamwork and its ability to create a better work environment for the workers and increase the level of creativity, productivity, and the success of the entire entity. Cohen (1999) says that teams are replacing individuals as the basic building blocks of an organization. In this century, teamwork skill has been taught as an essential educational concept at schools, so that students learn the proper strategies to develop professional skills as part of their educational process. The important professional skills such as solving conflicts, communication, collaboration, and positive interaction skills are noticeably being defined by managers as an important requirement for the work environment. So, employers and managers are always looking for individuals who can collaborate and work in teams as a critical skill in every working environment.
Competitiveness is an organizational style that is based on competition which relates to risk-taking, innovation, and change. Competitive dynamics have examined how the speed and the frequency of competitive actions that a firm takes and how the speed and frequency of rivals’ competitive actions influence a firm’s employee performance. Similarly, researchers have examined how the types of competitive actions that firms take to influence the likelihood and speed of response (Chen & Miller, 1994). They have also examined how the degree to which firms overlap in the markets in which they compete influences their competitive activity, including their entry and exit behavior (Chen, 1996; Baum & Korn, 1996). One of the main ideas in the competitive dynamics literature is that rival actions create incentives for firms to respond to maintain their competitive position (Chen & Miller, 1994). We extend this idea to the realm of customer satisfaction and argue that when rivals take actions aimed at increasing customers’ satisfaction, a firm has incentives to respond by improving its level of customer satisfaction. For example, if one MFB hires more cashiers to provide speedier check-out service, rivals in the same MFBs Institution may take steps to improve their service levels as well. Generally, if rivals improve their customer satisfaction, an MFB is likely to respond with actions to improve its customer satisfaction to defend its market share. Scholars have provided some evidence that employee competition positively affects customer satisfaction. However, the results are far from conclusive. Moreover, most of these studies use indirect measures of customer satisfaction, and none of the studies examine multiple dimensions of customer satisfaction.
The importance of organizational culture cannot be over-emphasized, it is all about living your company’s core values, whereby the internal and external identity of the company is defined.it has the power and capacity to turn employees into advocates. It is an avenue that helps the firm to retain its best employee to be functional and active and unite the various workforce as a team to be focused bound on achieving major set goals and objectives. The concept of teamwork as a cultural style has a strong influence on the performance of any organization and the employees who work in it.
Performance, According to the organizational goals, can be recognized as financial performance, or operational performance, and the dominant model in empirical strategy research is financial performance. It is based on financial indications that are assumed to reflect the fulfillment of the economic goals of the firm Venkatraiman, Ramanujam, (1986). Operational performance refers to non-financial dimensions and focuses on operational success factors that might lead to financial performance. It includes measures like product quality, circle time, and productivity. Effectiveness refers to the extent to which customer requirements are met Neely et al, (2005), measurement of overall effectiveness includes e.g. reputation, perceived performance, achievement of goals, survival, and needs for good knowledge about the organization and its industry. Employee performance is so common in management research that its structure and definition are rarely explicitly expressed, in general, performance, operational performance, and overall effectiveness (Hult et al. 2008).
Customers Satisfaction and employee performance can be accessed through this measure which involves mentoring, nurturing, and participation and is also referred to as extended family or large family. It is a working environment that is friendly, people have a lot in common. The leaders or executives are seen as mentors or maybe as father figures. It is held together by loyalty and tradition as great participation. Emphasis is on long-term human resources development and bonding colleagues by morale. Success here is defined within the framework of meeting client needs and caring for people. Some firms too might exhibit very creative or developmental organizational success which is based on risk-taking, innovation, and change, Quinn, and Spretzer (1991). It refers to the culture of an organization in entrepreneurial flexibility, innovative and creative areas with its external-oriented and dynamic structure. Employees can take the initiative supported with discoveries and freedom so they feel satisfied, happy, and successful in the environment. There are also formalized and structured work environments, procedures decide what people do. Leaders are proud of their efficiency-based coordination and organization. Keeping the organization functioning smoothly is most crucial. Formal rules and policies keep the organization together. The long-term goals are stability and results paired with the efficient and smooth execution of tasks. Trustful delivery, smooth planning, and low costs define success. In recent times, as a result of increased technology, innovations, improved business strategy, and marketing, companies are becoming more competitive within and across industries. The essence of this is to meet up with the pace of improved technology and increased market demand to enhance patronage to achieve organizational performance and still be relevant in business. This on the other hand can be sharpened and made possible by the adoption of a good blend of organizational cultures. So it is the culture of the organization that determines where the organization should be in expands of time.
Profitability can be achieved when Employees live up to avoid the major risk exposure in MFBs which is the risk of loss of income from loans due to processing errors, inadequate information, non-compliance with loan policies and excessive concentration of credit risks, counterfeit collateral, and employee fraud. One of the biggest control issues comes from the fact that the loan tracking system operates separately from the accounting system. For each loan facility that MFBs make, it exposes itself to credit risk with the client’s inability to repay the loan. This risk increases when employees collect inadequate information on the clients or when loan decisions do not comply with the stated policy. Common errors by employees are miscalculations e.g. Incorrect calculations of interest for loan payments, poor business analysis by loan officers e.g. overestimation of growth to result from the loan may likely occur in the process. However when all of these have been avoided all things being equal, the profitability of these banks is guaranteed, so employee performance translates into profitability.
1.2 Statement of the Problem
Organizations these days are working so had to ensure that there is a designed working organizational environment that will be conducive to effective and efficient employee service delivery that will lead to employee performance; hence the overall organizational performance. The MFB institution is not left out just like every other institution since it operates in a dynamic competitive environment and as such other institutions are continually reinventing themselves for better employee performance and the overall survival of the firm. This means for them to survive, they must come up with ideas that will be translated into plans and prospects and results, through reorientation, integration, training, and better salary packages to boost employee morals for optimal performance and then have a competitive advantage against their main competitors…
Albeit, every firm, or financial institution has some culture that is decipherable within it which it holds vital and also practices within the ambit of its rules and regulations that help in the modeling and control of its activities visa vice its human resources to tactically pursue and achieve its set goals and objectives.
The organizational culture of every firm is key in identifying the needs and courses required to equip employees to efficiently and effectively harness their potential optimally for the overall performance of Microfinance Banks.
Some decades ago, some Microfinance banks could not survive in microfinance institutions for some reasons attributed to very low employee performance. Quite a number of them were phased away for purposes of managerial incompetency.
But the trend seems to have been reversed, and such Microfinance banks employees in these contemporary times seem to be performing more and even aggressively competing with some seemingly weak commercial banks employees in terms of targeting the hitherto unbanked population that had been unreached over the years and other aspects of banking service delivery.
However, some scholars have attributed the ongoing high level of employees’ performance of MFBs to the adoption of a developed organizational culture that is consistent with modern-day banking practices. In recent studies by Wino and Francis (2019), and Owino et al. (2007) they found a positive relationship in their study that strong and dynamic cultures are important for superior employees’ performance because they promote consistency in organizational efforts. Although quite some studies have shown that a positive association exists as reported by Deal and Kennedy (1982). Peters and Waterman (1982), Densin and Mishra (1995), Olawyi (2017). For instance, Teamwork has been identified as organizational culture deliberated by some researchers as an essential occupational skill that is necessary to accomplish and achieve the visions, goals, plans, and objectives of the organization and to activate and enhance the performances of the workers and hence the overall performance. Jones et al (2007) state that understanding the impact of teamwork on performance is important because teamwork is viewed by some researchers as one of the key driving forces for improving employee performance. On the other hand or extreme contrary, Byles et al (1991) point it that strong or developed organizational cultures may not necessarily translate to improved employee performance especially when culture is inconsistent with critical success factors. No doubt, however, because the culture of the organization has to be geared towards the goal of the firm.
Despite these conflicting works of literature, whether or not organizational culture influences employee performance is an issue that has not been resolved. Furthermore, at the firms’ specific factors, there seem to be limited works of literature on the influence of organizational culture on employee performance of microfinance banks. Surprisingly most of the studies although relatively recent but were done in other countries of the world.
This prompted the researcher to do a study of the influence of organizational culture on employee performance of MFBs in Port Harcourt, Rivers State, to investigate if the ongoing high level of employee performance in the Institution is a result of developed organizational culture. Although the choice of studying MFBs that are in present Port Harcourt was for purpose of proximity. The investigation of the above issues will form the key problems in this research.
1.3 Conceptual FrameWork
To implement this study on organizational culture and employee performance of MFBs in Port Harcourt, the following measures (independent) and dimensions dependent) are used as shown above in a conceptual form.
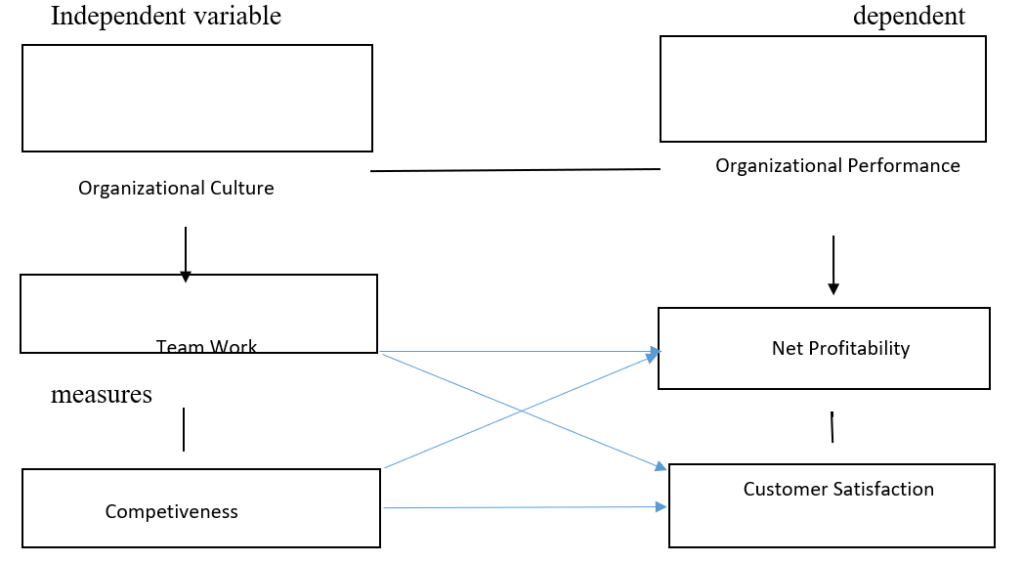
Source: conceptualized by the researcher 2019.
1.4 Aim and Objectives of the Study
The main objective of the study is to examine the influence of organizational culture on employee performance of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
Other objectives of the study are:
1) To examine the relationship between Team Work and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
2) To examine the relationship between Team Work and Customers Satisfaction of Micro Finance Banks in Port Harcourt.
3) To examine the relationship between Competitiveness and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
4) To examine the relationship between Competitiveness and Customer Satisfaction of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
1.5 Research Questions
The research questions that will guide this study are as follows:
1) Is there any significant relationship between Team Work and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt?
2) Is there any significant relationship between Team Work and Customer satisfaction of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt?
3) Is there any significant relationship between Competitiveness and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt?
4) Is there any significant relationship between Competitiveness and Customer Satisfaction of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt?
1.6 Research Hypothesis
Ho1: There is no significant relationship between Team Work and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
Ho2: There is no significant relationship between Team Work and Customer Satisfaction of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
Ho3: There is no significant relationship between Competitiveness and Net Profitability of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
Ho4: There is no significant relationship between Competitiveness and Customer Satisfaction of microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
1.7 Significance of the Study
This study shall be of great help to researchers, managers, and financial analysts.
1) Researchers – The findings of this study shall be significant and of great assistance to scholars by adding to the number of existing works of literature in the field so do doing be a guide to further research.
2) Managers – This study will provide managers with an in-depth insight into the connection between organizational culture and performance.
3) Financial Analyst- The findings of this work will help the financial analysts to understand that low or high organizational performance could be traceable to weak and strong adopted organizational culture and internal administrative styles of microfinance banks and financial institutions.
1.8 Scope of the Study
The content scope -The research work will focus on the influence of organizational culture which shall be measured using Team Work, Competitiveness and Employee Performance measured using Net profitability and Customer Satisfaction.
Geographical Scope– the study is designed to cover some selected microfinance banks in Port Harcourt.
Level of Analysis– the study is at the level of micro and will assess individual unit members since our dependent variables center on employee performance.
Unit of Analysis -the study will cover a sample frame comprising primarily of managers, customer desk staff, cashiers, marketers, and other staff of the organization, given the nature of the variables of the study.
1.9 Limitations of the Study
The study was limited by the conditions stated below however; the study achieved its objectives.
1) Data gathering was difficult.
2) The use of proxies that may not capture exactly what was intended to measure.
3) The study is limited to primary data
4) Some quantitative variables used will be measured with the qualitative scales.
5) The privilege of access to managers and staff of some microfinance banks during the author’s field survey was a serious challenge since some managers feared that such information could be used against them.
1.10 Definitions of terms
Organization culture: is defined as the underlying beliefs, assumptions, values, and ways of interacting that contribute to the unique social and psychological environment of an organization.
Employee Performance: according to the Cambridge English dictionary, it is defined as how well a person, machine, etc. does a piece of work or activity. It is also known as the accomplishment of a given task measured against preset known standards of accuracy, completeness, cost, and speed.
Customer Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction is defined as the level of fulfillment that a customer derives from doing business with a firm.
Production: this is defined as a measure of the efficiency of a person, machine, factory, system, etc in converting inputs into useful outputs.
Profitability: the degree to which a business or activity yields profit or financial gain. It is also defined as the ability of a business to earn a profit.
Return on asset: this is an indicator of how profitable a company is relative to its total assets. ROA gives a manager, analyst, and investor an idea of how efficient a company’s management is at using its assets to generate earnings. It is displayed as a percentage.
Quantitative Variable: these are variables that are measured on a numeric or quantitative scale. Ordinal, interval, and ratio scales are quantitative, Variables whose values result from counting or measuring something.
1.11 Organization of the study
This study is organized into five chapters;
Chapter one consists of the introduction, statement of the problem, conceptual framework, research questions, research hypothesis, the significance of the study, limitations of the study, and definitions of terms.
Chapter two presents the literature review of important literature and researchers related to the study.
Chapter three presents the research methodology.it describes the research design sampling procedure, questionnaire design, data collection, and data analysis techniques.
Chapter four is mainly concerned with the presentation and analysis of data. The hypothesis stated in chapter one was tested here leading to the findings of the research organizations. Chapter five shows the final study consisting of discussion, conclusion, and recommendations.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.